We point out L-band rather a lot right here at SparkFun, from our RTK Side L-band to our RTK mosaic-x5, which boasts triband reception. Lately on the weblog, we mentioned the fundamentals of what it’s, however did not get to why we use it – we saved that for right this moment! Buckle in for a historical past lesson.
L-band has been essential within the improvement of GPS, serving to to rework it from a navy software to the ever-present navigation assist we depend on right this moment. As we speak we’ll chart the journey of L-band, from its early adoption in GPS programs to its position within the high-tech positioning {hardware} we use now. We’ll discover how this slice of the radio spectrum has been the spine of GPS, supporting its progress and making certain that getting misplaced is, properly, a factor of the previous. Able to get a clearer sign on how the L-band has steered the course of GPS historical past? Let’s dive in!
L-Band and GPS
We use L-Band for america’ satellite tv for pc based mostly navigation system, GPS. “L-Band” is a descriptor for the continual band of radio frequencies from 1 GHz to 2 GHz. So in case your radio is transmitting at 1575.42 MHz, you might be transmitting on L-Band. America’ GPS is transmitted on frequencies starting from 1176.45 MHz (L5) to 1575.42 MHz (L1), whereas different GNSS constellations such because the European Union’s GALILEO and China’s BEIDOU, have their very own frequencies inside the L-Band. This brings up a query: Why do all of those completely different GNSS programs, from all completely different nations, use L-Band? What makes it such a fascinating band for GNSS?
A Very Transient Historical past of Satellite tv for pc Navigation
In 1957, the USSR launched the world’s first satellite tv for pc, Sputnik 1. Sputnik contained a small radio station referred to as the D-200, designed to transmit temperature and strain data measured by sensors within the physique of the satellite tv for pc. The D-200 ran on three silver-zinc batteries, which saved it transmitting for 21 days, or roughly 314 orbits across the Earth. This telemetry information was transmitted utilizing a quite simple and sturdy protocol; Threshold Encoding for the worth, and On-Off Keying for the state. Scientists and engineers predetermined completely different thresholds of temperature and strain that might be important, then arrange a bit sample that corresponded to every threshold. The radio would use On-Off Keying to sign whether or not every threshold was met or unmet. On-Off keying is a literal communications protocol, the place the presence of a service wave signifies a one, and its absence signifies a zero. The radio transmitted at 20.005 MHz as a main, and 40.005 MHz as a supplementary channel. The selection of those particular frequencies mirrored a steadiness between technical feasibility, the necessity for dependable information transmission, and the need to facilitate widespread participation within the satellite tv for pc’s monitoring and monitoring by each skilled stations and radio amateurs worldwide.

The launch of Sputnik signaled (pun supposed) the start of the house race, and scientists and radio lovers all over the world started monitoring the indicators it was transmitting. William Guier and George Weiffenbach of John Hopkins College’s Utilized Physics Laboratory had been two such scientists. As a part of his Ph.D. dissertation in microwave spectroscopy, Guier had entry to a excessive precision radio receiver. Utilizing this receiver, and the close by WWV Beltsville radio station’s 20 Mhz service sign, Guier and Weiffenbach had been capable of subtract the 20 Mhz WWV sign from the 20.005 MHz Sputnik sign, yielding a 5 KHz sign – which was within the audible frequency vary. They might now “hear” to the transmissions from Sputnik. As they listened to the transmission, they realized that the sign was wandering because the craft handed overhead; when it was coming in direction of their location, the tone began out excessive, then grew to become decrease and decrease, till they misplaced sign.
They rapidly deduced that they had been listening to the Doppler Shift of the sign, a modulation of frequency attributable to relative velocities; by enjoying the audible sign via a wave analyzer, they created a frequency/agenda. With this information, they had been capable of calculate the orbital interval of the craft to a excessive accuracy. With some refinement, this calculation was capable of decide all the orbital parameters of the satellite tv for pc. This analysis caught the discover of Dr. Frank McClure, the Director of APL’s Analysis Middle. He realized that this methodology could possibly be inverted; as a substitute of figuring out the placement of the satellite tv for pc based mostly on the receiver’s place, the inverted calculation might decide the receiver’s place based mostly on the placement of the satellite tv for pc. Dr. McClure started engaged on this challenge, and by the Spring of 1958 had despatched out a proposition for a grant challenge to create a satellite tv for pc based mostly navigation system for the US Navy; this challenge would finally flip into the Navy Navigation Satellite tv for pc System (NNSS).
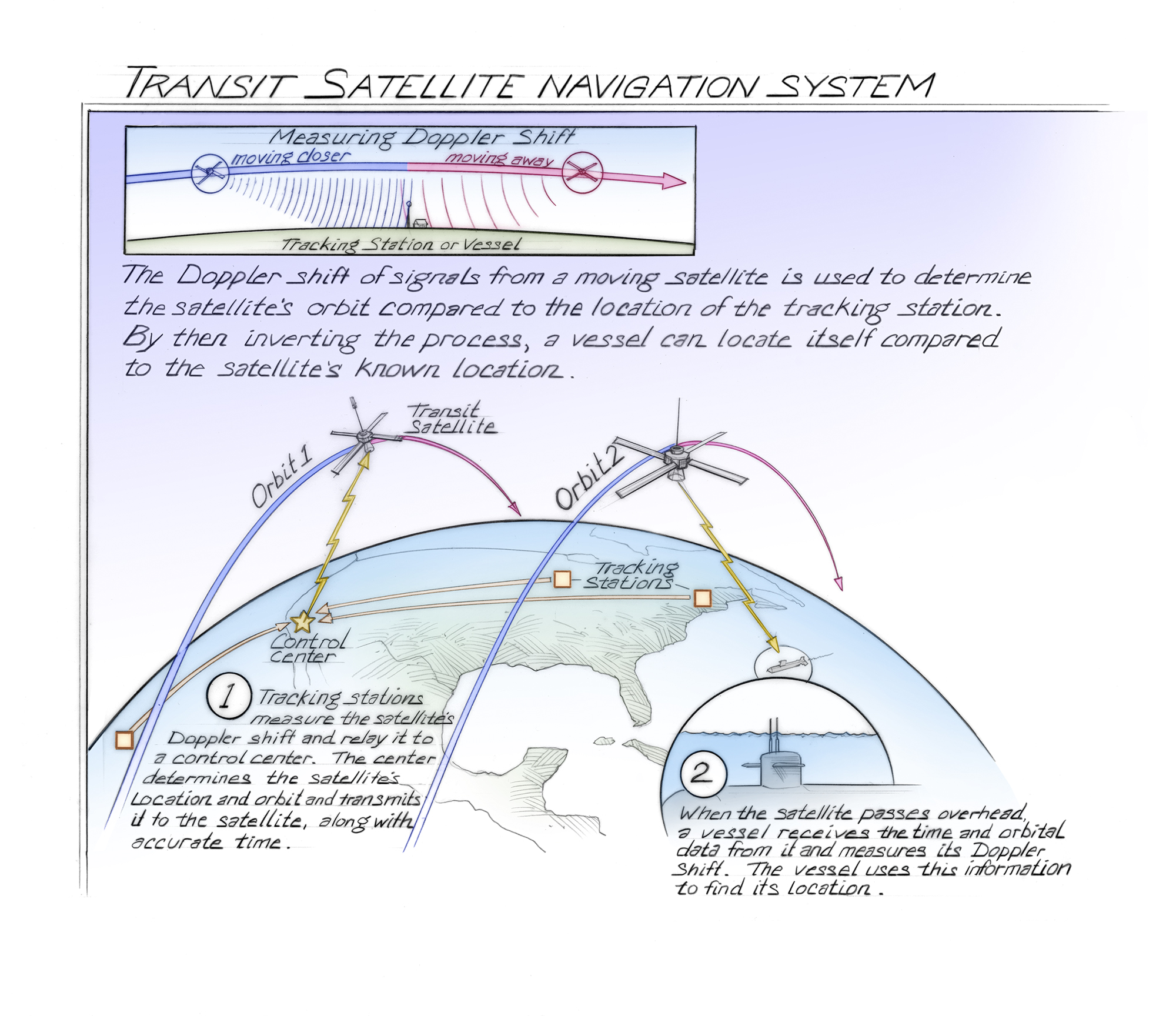
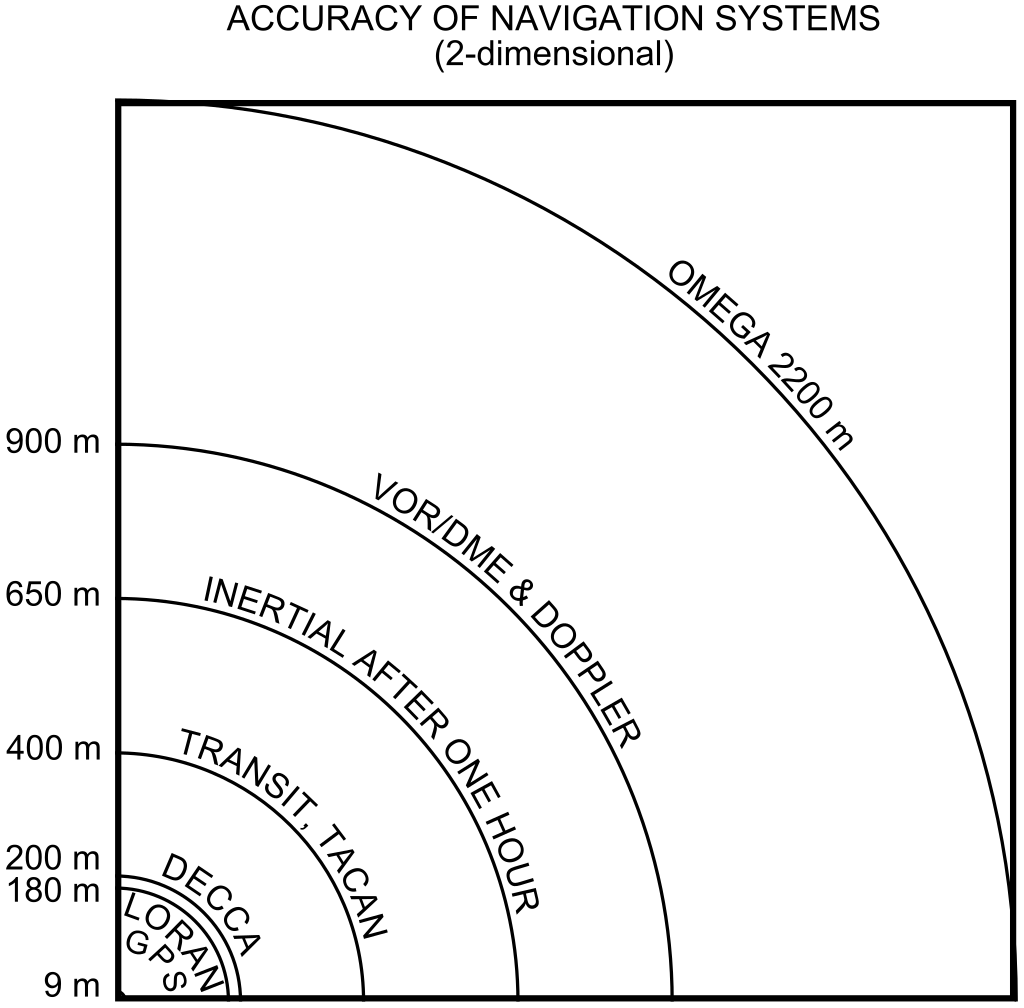
The NNSS used Transit satellites, and was the primary satellite-based navigation system; design for the system started in 1958 and it entered service in 1964. The satellites used for the NNSS transmitted at each 150 MHz and 400 MHz, properly beneath the L-Band, and receivers used the Doppler Impact to triangulate their very own place. The first use of the NNSS by the US Navy was to assist its Polaris ballistic missile submarine fleet. Nonetheless, the accuracy of the NNSS in its authentic type was low, and solely supplied a two dimensional latitude/longitude place. There have been a complete of 5 Transit satellites, so getting the best accuracy place repair potential (200 meters) might take over an hour. To enhance accuracy, a brand new part was wanted: time. By broadcasting an extra timing sign to receivers, they may add the timing distinction between their location and the Transit satellite tv for pc to the place calculation. Two further satellites had been launched, referred to as Timation satellites, in an effort to resolve this drawback.
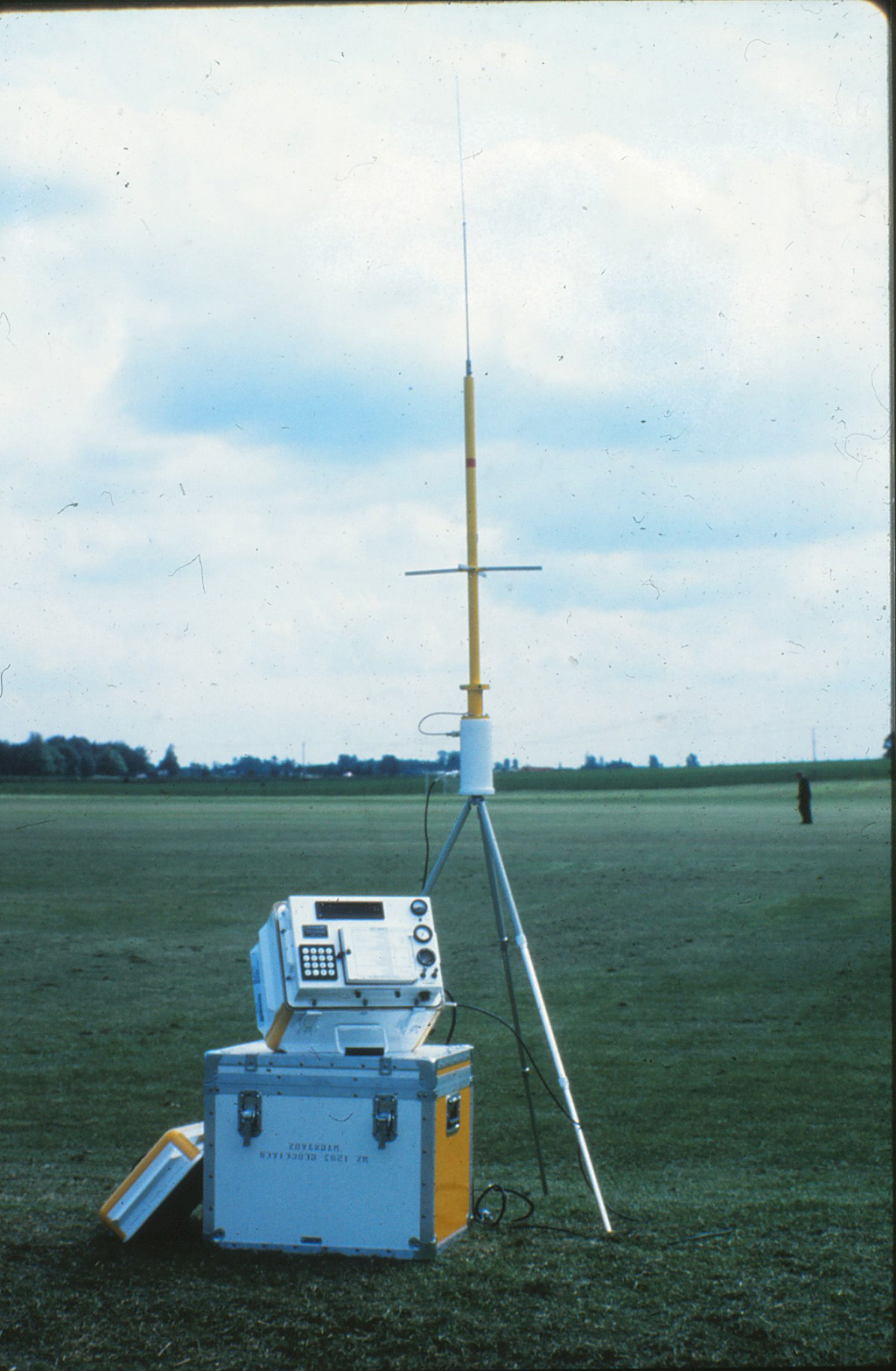
The Timation satellites proved to achieve success, rising the theoretical accuracy of the NNSS to 1 meter (although this took a number of days of information assortment and costly receiver gear to do). In 1967 US Vice President Hubert Humphrey declared that the system was operational for civilian use, the place it grew to become closely built-in into oceanic transport industries, surveying, and civil engineering; after the discharge to the civilian world, it grew to become generally referred to as “Transit” or “NavSat”. Transit had a big impact on the surveying trade, revolutionizing the instruments they used; surveyors now carried Doppler survey receivers, referred to as georeceivers, which had been used to ascertain the WGS 84 reference coordinate system that we nonetheless use to at the present time. In 1974, the Soviet Union started launching its personal navigation satellites for a system referred to as Parus. Parus makes use of the identical precept (and related frequencies) as NNSS, and continues to be in service as of 2024.
The NNSS was revolutionary for Naval navigation however supplied low accuracy, lengthy ready intervals between place fixes, and required costly receiver gear. To resolve these points, new programs had been designed. An early (and vital) try codenamed 621-B, launched in parallel with the Timation challenge, was designed by the US Air Pressure through the mid 60’s. 621-B explored many superior digital sign transmission and processing prospects, together with the idea of pseudorandom noise to extend resistance to jamming and crosstalk with different navigation satellites. The concept with pseudorandom noise was that every satellite tv for pc could possibly be coded with a Psuedo Random Quantity (PRN); this quantity is used to introduce digital noise into the sign in a manner that’s repeatable with out interfering with PRN’s from different satellites. This scheme basically permits the frequency band to be multiplexed, with many transmitters all functioning in unison.
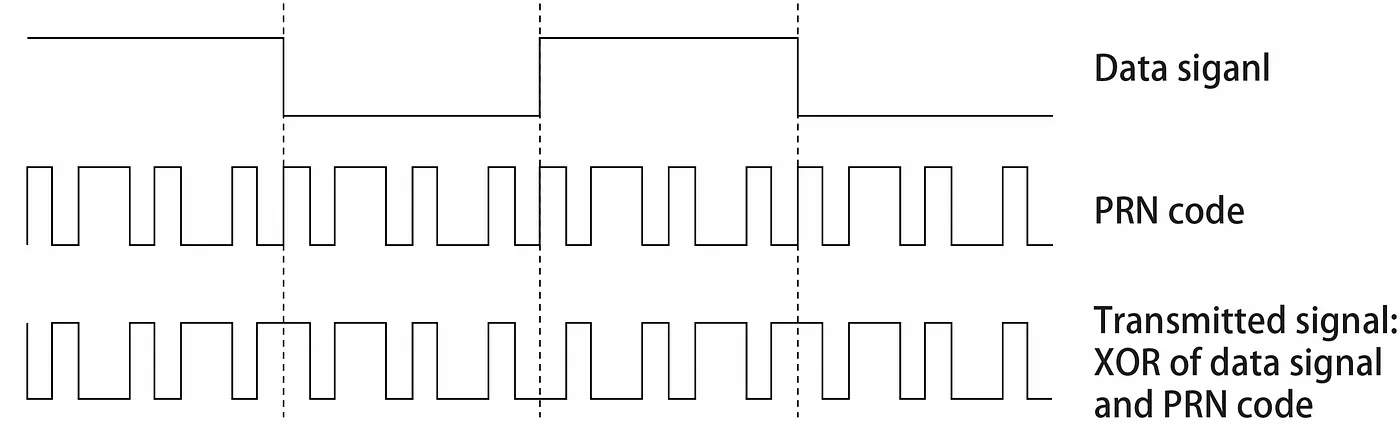
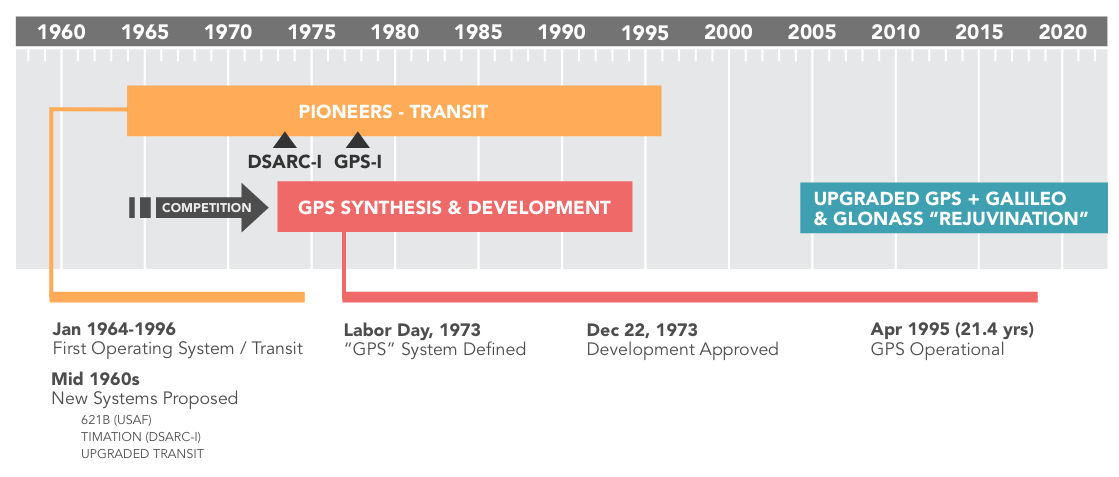
The International Positioning System, or GPS, was a US Division of Protection challenge began within the early 1970’s to design a greater satellite tv for pc based mostly navigation system. GPS design was based mostly on lessons-learned from earlier designs; the inverse orbital place calculations of Transit, the time corrections of Timation, and the idea of digital sign PRN from challenge 621-B. One of many key targets was to permit for a 4 dimensional repair for receivers; to find out latitude and longitude, altitude, and time.
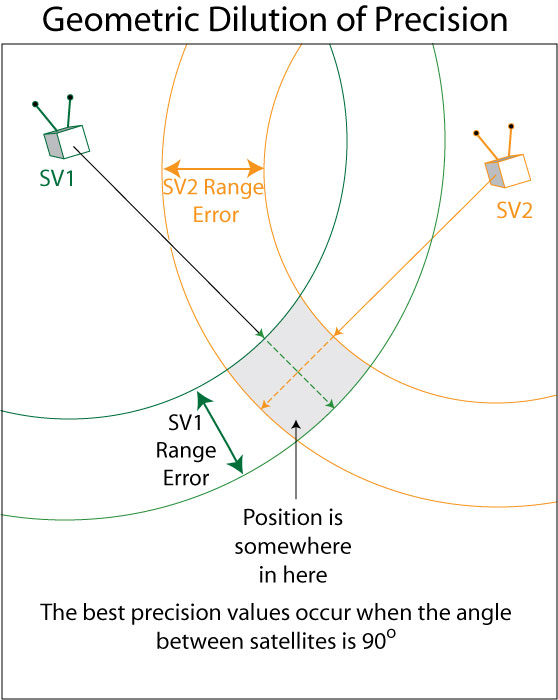
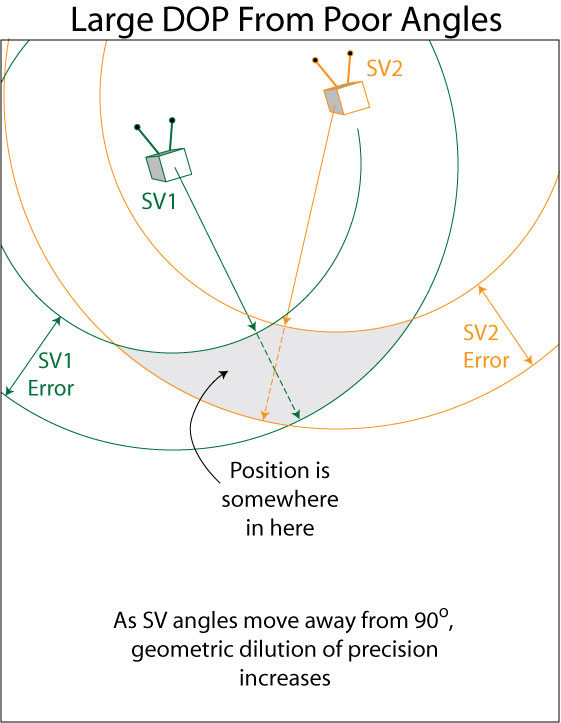
The primary eleven GPS satellites had been launched in 1978. The system was designed to have 24 operational satellites in whole, organized into six completely different orbital planes to maximise availability and precision. Having a number of orbital planes permits for higher geometry between the receiver and the satellites; this geometry lowers the Dilution of Precision (DOP) of the place calculation. The launches had been carried out in “Blocks”; the primary three Blocks had been manufactured by Rockwell Worldwide, a complete of 39 satellites launched over 19 years. GPS grew to become the primary satellite tv for pc based mostly navigation system to make use of the L-Band for transmission. Since GPS was launched, many different GNSS constellations have been launched that additionally use L-Band. This brings us full circle again to the query: Why L-Band?
Why L-Band?
The collection of frequencies for GPS was a fancy drawback; the price of satellites and receivers needed to be low, the scale of apparatus small, and the indicators detectable at a really lengthy vary, via a wide range of environments. The Earth’s ionosphere offered challenges, in addition to rain and snow. The chief architects and builders of the system had been Bradford Parkinson, Roger Easton, and Ivan Getting; however the engineering that determined the frequency to make use of was accomplished by Frank Butterfield of the Aerospace Company.
Butterfield wrote a paper in 1976 titled “Working Frequencies for the NAVSTAR/International Positioning System” which laid out what frequency would work greatest for the GPS system, and why. A quote straight from that paper’s Abstract part explains it very clearly:
The NAVSTAR/GPS navigation sign frequency selections are constrained on the low aspect by efficiency limitations and by frequency allocation actions of earlier years. They’re restricted on the higher aspect by the price of satellites in orbit.
Most radio band allocations at the moment had been beneath the 1000 to 2000 MHz L-Band, similar to FM radio (88-108 MHz), HAM radio (1.6-1240 MHz), Broadcast Tv (44-294 MHz). Being greater than these broadly used frequencies, there could be a lot much less interference to sift via to seek out the weak GPS indicators, which might enable for a extra exact and correct repair. A further drawback with decrease frequencies is that they expertise extra pronounced results of ionospheric propagation delay; that’s, as they encounter the ionosphere, they expertise reflection, refraction, diffraction, and scintillation. A few of the electromagnetic vitality is mirrored on the boundary layer between vacuum and ionospheric plasma, bouncing again into house.
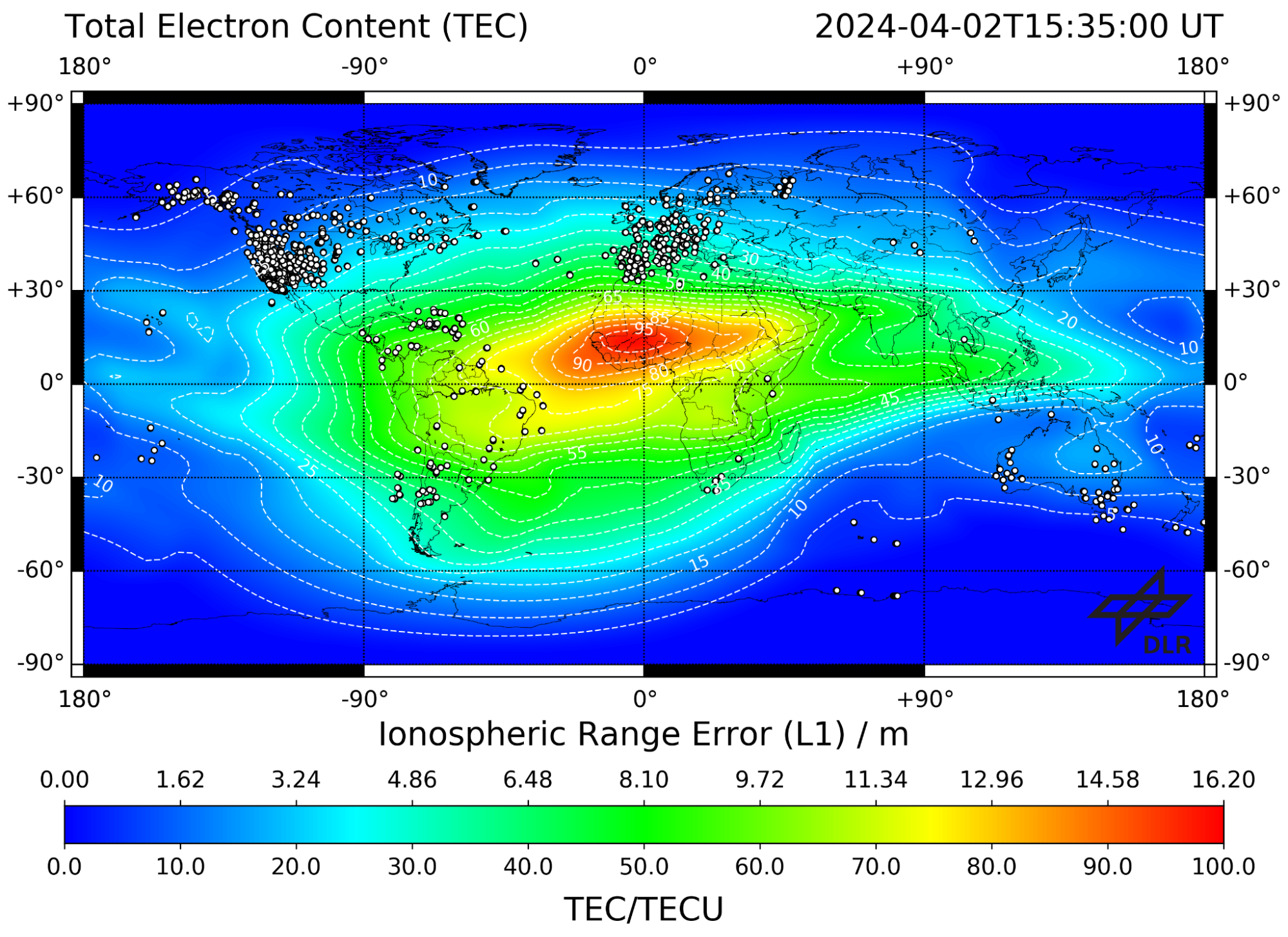
This boundary layer additionally causes refraction and diffraction, altering the velocity and path of propagation, just like a laser “bending” because it shines via an aquarium. Scintillation is an impact attributable to density variations within the plasma; these density variations trigger completely different quantities of refraction within the wave, inflicting components of the wave to overlap and intrude constructively or destructively. This interference causes the electromagnetic energy of the service wave to fluctuate.
- The Ionospheric Impact
- The ionosphere has an inconsistent electron density, and the electron density determines many properties of how the radio wave behaves because it passes via.
The interplay with the ionosphere causes sign group delay, a sign processing time period for the propagation delay launched by refraction. Because the wave encounters a change within the refractive index of the medium it propagates via (similar to shifting from a vacuum into ionospheric plasma), the transmission velocity modifications. This modification of velocity modifications the angle of propagation as properly; it is a basic instance of Snell’s legislation and Conservation of Momentum.
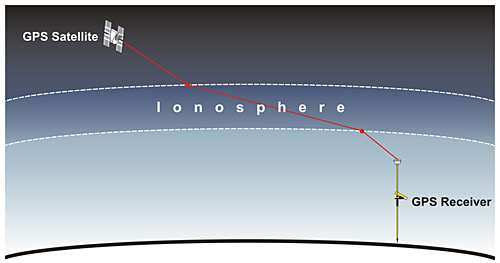
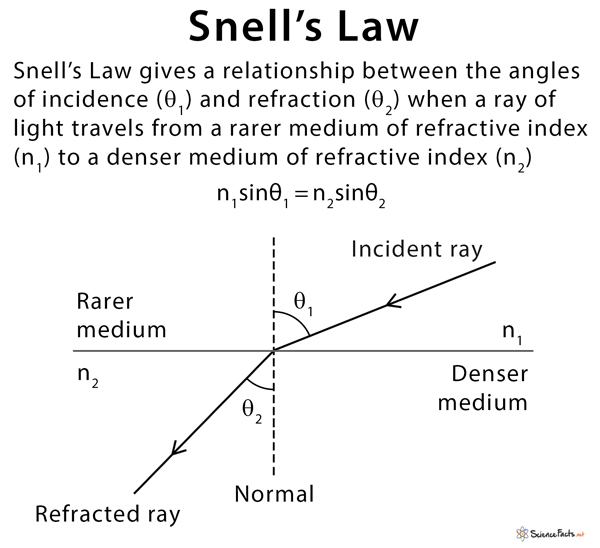
An fascinating attribute of radio waves (and light-weight generally) is that as they move from one medium to a different, the wavelength modifications (due to the change in velocity) whereas frequency stays the identical. It follows that the angle of refraction is inversely proportional to wavelength; because the wavelength of sunshine decreases, the refractive index will increase, inflicting the angle of refraction to change into smaller. The decrease the frequency chosen for GPS indicators, the higher the refraction angle could be, the more serious the accuracy of the system could be.
If decrease frequencies introduce higher error, why not select a really excessive frequency sign? Effectively, wavelength additionally determines how properly the sign can move via or round varied media. Very excessive frequencies wouldn’t have the ability to penetrate properly via miles of rain and snow, via tree canopies, via the roof of a automobile.
The system wanted to be sturdy, capable of perform in all kinds of environments and places. A secondary motive was value of apparatus. Receivers wanted to be low cost sufficient for big scale manufacturing, and this challenge was already demanding a big price range given the deliberate 24 GPS satellites. Dependable excessive frequency parts had been very costly, and had been much more costly to launch into house.
So there you have got it, why L-band is used for Satellite tv for pc Navigation – we would have liked to steadiness the precedence for a excessive frequency that might be impervious to interference within the ionosphere and from the environment, whereas additionally balancing value of apparatus.
The method of allocating L-band frequencies for GPS indicators was like a high-stakes recreation of Tetris, however as a substitute of becoming blocks collectively, it concerned becoming a myriad of worldwide pursuits and technical constraints right into a coherent spectrum coverage. The L-band is a candy spot for satellite tv for pc communication as a result of its steadiness between vary and precision. Nonetheless, it is also prime actual property for different providers, resulting in a fancy and infrequently contentious allocation course of. The method concerned intricate negotiations and regulatory wrangling, typically mediated by worldwide our bodies just like the Worldwide Telecommunication Union (ITU). These organizations needed to steadiness nationwide safety issues, given GPS’s origins as a navy expertise, with the burgeoning potential for civilian functions that would revolutionize navigation, agriculture, and extra.
The allocation was not nearly discovering an empty slot within the spectrum; it was about making certain that the frequencies used for GPS wouldn’t intrude with current providers and could be protected against future encroachments. This led to the institution of particular frequency bands for GPS use, with cautious consideration of technical parameters like sign power and interference thresholds. As GPS expertise advanced and have become built-in into just about each facet of contemporary life, the significance of those allotted frequencies solely grew. The method additionally set a precedent for the way international spectrum allocation could possibly be managed within the face of competing pursuits and technological developments. In essence, the allocation of L-band frequencies for GPS was a masterclass in worldwide cooperation, technical evaluation, and forward-thinking policy-making.
Sources and Additional Studying:
I additionally discovered a pdf of the unique engineering design doc for the radio system aboard Sputnik, however it’s in Russian and the one translation system I’ve been capable of get working with it’s textual content solely…
This supply will possible not give you the results you want; I ended up discovering a VPN server in Russia to get entry
You most likely use GPS on a regular basis, what else do you wish to find out about the way it works? Tell us within the feedback!

