Osaka College researchers have found why AR fails indoors and proposed an answer—learn the way it may change every part!
Augmented actuality (AR) apps on smartphones are top-rated. They allow you to see issues like how furnishings would look in your house, enable you to use maps higher, or allow you to play enjoyable video games. A well-known instance is Pokémon GO, the place you catch digital creatures along with your telephone. However when you attempt to use AR apps inside a constructing, they won’t work as a result of the know-how has bother with no robust GPS sign.
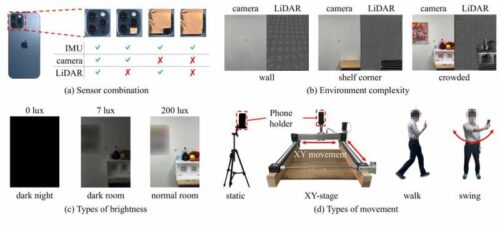
After conducting thorough experiments with smartphones and customers, researchers from Osaka College have uncovered the detailed causes behind these issues and proposed a attainable answer.
To judge the efficiency of those programs, researchers performed case research, together with establishing a digital classroom in an empty lecture corridor, the place members had been tasked with arranging digital desks and chairs in an optimum structure.
113 hours of experiments and case research had been performed throughout 316 patterns in real-world settings. The aim was to determine and analyze AR failure modes by selectively disabling particular sensors and altering environmental and lighting situations.
The examine revealed that digital components in augmented actuality usually “drift” throughout the scene, which might trigger movement illness and diminish the sense of realism. The findings confirmed challenges with visible landmarks, that are arduous to detect from a distance, at excessive angles, or in low-light situations. LiDAR will also be unreliable, and the inertial measurement unit (IMU) accumulates errors at excessive and low speeds over time. To beat these points, the researchers recommend utilizing radio-frequency-based localization, akin to ultra-wideband (UWB) sensing, as a attainable answer.
Extremely-wideband (UWB) features equally to WiFi or Bluetooth, with in style purposes together with Apple AirTag and Galaxy SmartTag+. In contrast to vision-based landmarks like QR codes or AprilTags, radio-frequency localization is much less influenced by lighting, distance, or line of sight.
Researchers anticipate that sooner or later, UWB or different sensing applied sciences akin to ultrasound, WiFi, BLE, or RFID could possibly be mixed with vision-based strategies, leading to considerably enhanced augmented actuality purposes.
Reference: Expertise: Sensible Challenges for Indoor AR Functions, DOI: 10.1145/3636534.3690676
👇Observe extra 👇
👉 bdphone.com
👉 ultraactivation.com
👉 trainingreferral.com
👉 shaplafood.com
👉 bangladeshi.assist
👉 www.forexdhaka.com
👉 uncommunication.com
👉 ultra-sim.com
👉 forexdhaka.com
👉 ultrafxfund.com
👉 ultractivation.com
👉 bdphoneonline.com



